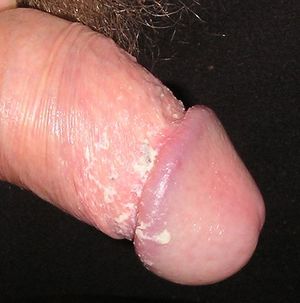
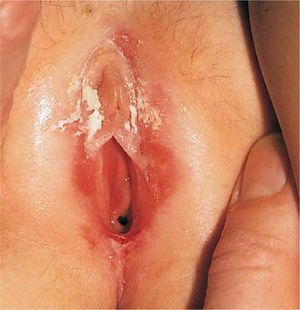
Smegma
(Dieser Artikel wurde noch nicht aus dem Englischen übersetzt oder enthält noch englische Textpassagen. Bitte beziehe dich vorerst auf die Informationen im englischen Artikel. Klicke dazu in der IntactiWiki-Navigation im Abschnitt "In anderen Sprachen" auf "English".)
Smegma' is the name given to a flaky material that accumulates underneath the foreskin in males, and underneath the clitoral hood and within the labial folds in females. In males, it is composed of secretions of ectopic sebaceous glands in the foreskin, mixed with secretions of the prostate, seminal vesicles, mucin from the urethral glands, and desquamated epithelial cells.[1][2][3]
Smegma was believed to be carcinogenic
Circumcision advocates of the past who alleged a relationship between "lack of circumcision" and genital cancers formerly implicated smegma or smegma-borne pathogens as the causative agent. Only two histologic studies of human smegma have ever been conducted, both of which found it to be perfectly harmless.
The hypothesis that human male smegma is carcinogenic was first formulated in 1932 by circumcision promoter Abraham L. Wolbarst, M.D.[4] Wolbarst also believed that circumcision prevented epilepsy. (In the early part of the 20th Century, the paroxysm of masturbation in children was often misidentified as an epileptic seizure.) He wrote: "[Circumcision] diminishes the tendency to masturbation, convulsions and other reflex phenomena of local irritation."
No laboratory or clinical research had been done on the subject at the time. Regardless, Wolbarst's hypothesis about smegma and cancer found its way into early medical textbooks. In the 1950s a few experiments were done to test the hypothesis by injecting horse smegma into wounds made in the backs of mice. There were clinical studies that attempted to induce cancer by introducing smegma subcutaneously and intravaginally: No carcinomas could be induced.
The smegma hypothesis was finally disproven by an exhaustive study by Reddy in 1963.[5] His results were: "The conviction that human smegma is a carcinogen could not be substantiated."
Siehe auch
Einzelnachweise
- ↑
 Parkash, S., et al. Sub-Preputial Wetness - Its Nature. Ann Nat Med Sci (India). 1982; 18(3): 109-112. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
Parkash, S., et al. Sub-Preputial Wetness - Its Nature. Ann Nat Med Sci (India). 1982; 18(3): 109-112. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
- ↑
 Hyman, A.B., Brownstein, M.H.. Tyson's
Hyman, A.B., Brownstein, M.H.. Tyson's Glands
. Archives of Dermatology. Januar 1969; 99(1): 31-37. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019. - ↑
 Van Howe, R.S., Hodges, F.M.. The carcinogenicity of smegma: debunking a myth. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006; 20(9): 1046. DOI. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
Van Howe, R.S., Hodges, F.M.. The carcinogenicity of smegma: debunking a myth. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2006; 20(9): 1046. DOI. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
- ↑
 Wolbarst, A.L.. Circumcision and Penile Cancer. The Lancet. 16. Januar 1932; 1(5655): 150-153. DOI. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
Wolbarst, A.L.. Circumcision and Penile Cancer. The Lancet. 16. Januar 1932; 1(5655): 150-153. DOI. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
- ↑
 Reddy, D.G., Baruah, I.K.. Carcinogenic action of human smegma. Archives of Pathology. April 1963; 75(4): 414-420. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.
Reddy, D.G., Baruah, I.K.. Carcinogenic action of human smegma. Archives of Pathology. April 1963; 75(4): 414-420. Abgerufen am 16. Oktober 2019.